最小环
Contents
定义
最小环:指图中的一个环,它不包含任何更小的环。
在无向图中,最小的最小环为3个节点。在有向图中,最小的最小环为2个节点。(不考虑self-loop的情况)
无权无向图求最小环
例题: https://codeforces.com/contest/1364/problem/D
题意
给定一个 connected undirected graph:
$n$个vertex, 和一个int $k$, 其中 $3 \leq k \leq n$, 请找出 以下的其中之一:
-
一个独立集(set of vertex, 两两之间没有edge), 包含 $\lceil\frac{k}{2}\rceil$ 个vertex
-
一个simple cycle (set of vertex, 不包含重复vertex), 其中 $len \leq k$
题解
-
如果这是一个tree ($m = n-1$), 则 (1)很容易找, 只要dfs一下,做一个图的染色 (染成 $0,1$)即可, 最后取 全部的 $0$ 或者 全部的 $1$
-
如果不是tree, 必然存在cycle, 那么我们可以找到一个最小环, 最小环必然满足 (1) 或者 (2)!(易证)
•怎么找最小环? 用DFS!
- 维护一个环的长度
len - 维护一个
dep[]数组, 代表每个vertex的depth - 维护一个
pre[]数组,pre[u]代表dfs过程中 u的parent - 维护一个
int c, 代表找到的cycle的 终点!
然后,
-
从vertex 1开始dfs,
dep[to] = dep[cur] + 1这样来更新dep[] -
当我们找到一个backward edge时, 更新最小环长度
len = min(len, abs(dep[to] - dep[cur]) + 1))并且更新
c, 使得c = cur, 然后继续探索! -
dfs结束后, 直接用
vector<int> cycle; void findcycle() { while (len--) cycle.push_back(c), c = pre[c]; }即可找到最小环!
时间复杂度:$O(n+m)$
无权有向图求最小环
例题:https://atcoder.jp/contests/abc142/tasks/abc142_f
题意
给定一个 directed graph,求它的一个 subgraph 满足:
- $V'$ 是 $V$ 的 non-empty subset
- $E'$ 是 $E$ 中,所有两端均在 $V'$ 内的edges
- $V'$ 中,所有的 vertex 的 in-degree 和 out-degree 均为1
题解
易知,最小环满足这个条件!
如何求最小环?可以用 $N$ 次 DFS!
- 维护
ed代表环的终点,维护最小环长度final - 维护一个
dep[]数组, 代表每个vertex的depth - 维护一个
par[]数组,par[u]代表dfs过程中 u的parent - 维护一个
in[]数组,代表在dfs过程中,当前的某个vertex是否存在于递归stack中!
dfs过程如下:
int n,m, dep[maxn], par[maxn];
int ans = 1e9, ed = -1, final = 1e8;
vector<int> cycle;
bool in[maxn];
void dfs(int cur) {
in[cur] = 1;
dep[cur] = dep[par[cur]] + 1;
for (int e = head[cur]; e; e = edges[e].nxt) {
int to = edges[e].to;
if (dep[to]) {
if (in[to]) { // 必须得在递归栈内
int res = abs(dep[cur] - dep[to]) + 1;
if (res < ans) {
ans = res;
ed = cur;
}
}
} else {
par[to] = cur;
dfs(to);
}
}
in[cur] = 0;
}
为什么要加
in[]数组?
如下图:
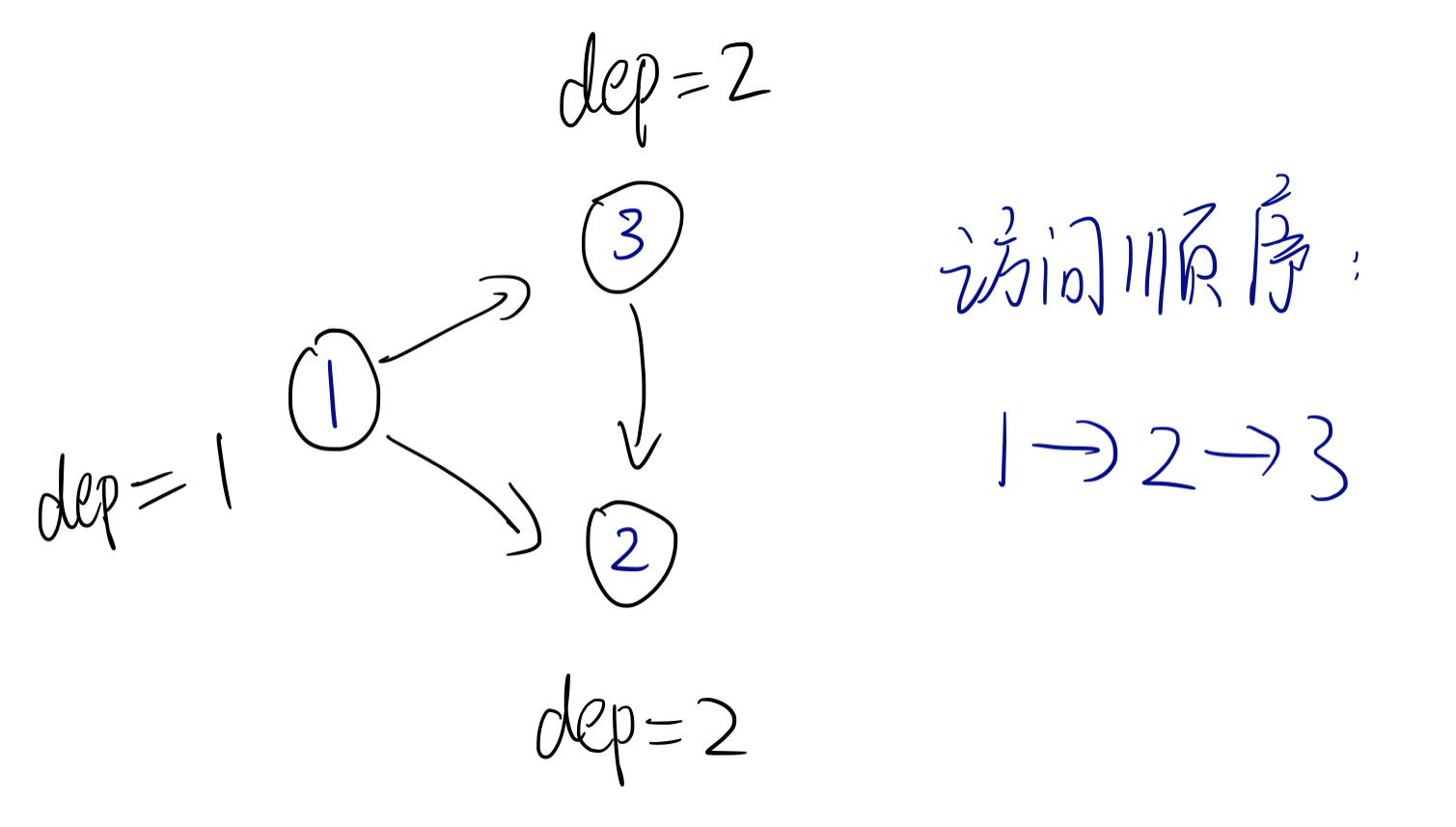
我们需要保证这个环必然全部同时出现在递归stack内,否则可能会出问题!
(如上图,如果不考虑 in[] 数组的话,就有可能错误的把 1->3->2 当作一个环!
为什么要使用 $N$ 次 dfs ?
如下图:
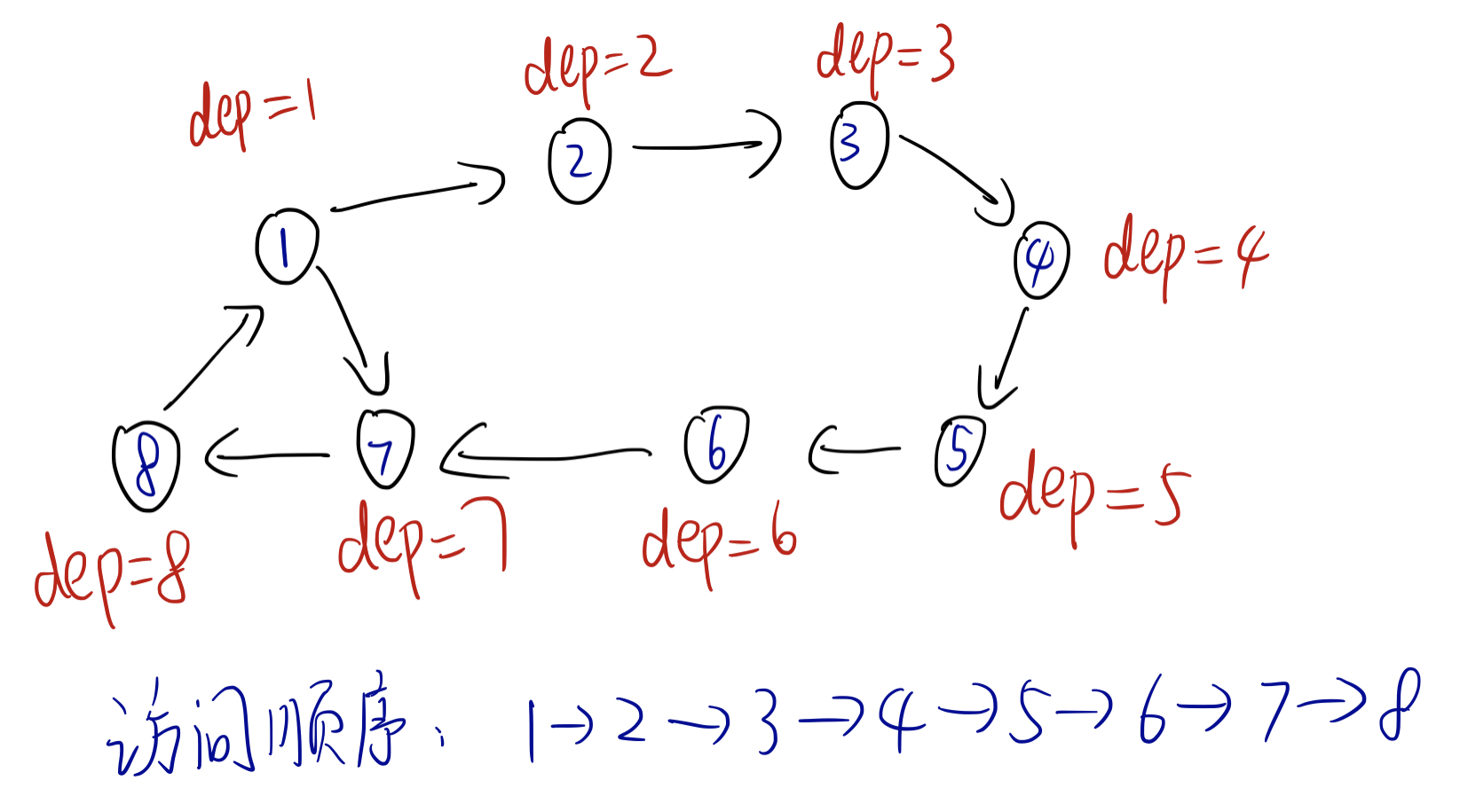
如果我们从 $1$ 开始进行 dfs,那么如果是按照图上的访问顺序,会导致我们找不到最小环!
但是如果从 $7$ 开始进行 dfs,就可以找到了!
所以我们需要每一个点都开始一次dfs,总共 $N$ 次 dfs。
注:优化:可以在每次dfs中找到的环中找最小环,如果不是环中的节点,就不需要考虑了。
代码
using namespace std;
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define abs(a) ((a>0)?a:-(a))
const int mod = 1e9+7;
const int maxn = 1e3+5;
const int maxm = 2e3+10;
struct Edge {
int to,nxt;
} edges[maxm];
int head[maxn], ecnt = 1;
int n,m, dep[maxn], par[maxn];
int ans = 1e9, ed = -1, final = 1e8;
vector<int> cycle;
bool in[maxn];
void add(int u, int v) {
Edge e = {v, head[u]};
edges[ecnt] = e;
head[u] = ecnt++;
}
void init() {
cin >> n >> m;
for (int i = 1; i <= m; i++) {
int u,v; cin >> u >> v;
add(u,v);
}
}
void dfs(int cur) {
in[cur] = 1;
dep[cur] = dep[par[cur]] + 1;
for (int e = head[cur]; e; e = edges[e].nxt) {
int to = edges[e].to;
if (dep[to]) {
if (in[to]) {
int res = abs(dep[cur] - dep[to]) + 1;
if (res < ans) {
ans = res;
ed = cur;
}
}
} else {
par[to] = cur;
dfs(to);
}
}
in[cur] = 0;
}
void renew() {
fill(dep, dep+n+1, 0);
fill(par, par+n+1, 0);
fill(in, in+n+1, 0);
ans = 1e9;
}
int main() {
fastio;
init();
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
dfs(i);
if (ans < final) {
final = ans;
cycle.clear();
while (ans--) cycle.push_back(ed), ed = par[ed];
}
renew();
}
if (final == 1e8) cout << -1 << endl;
else {
cout << final << "\n";
for (int a : cycle) cout << a << "\n";
}
}
有权图求最小环
Floyd $O(n^3)$ 可求!
无向图/有向图找环
无向图找环
如果有重边的话,dfs记录的应该是parent的边,而不是点!
vector<int> cycle;
void dfs1(int u, int in_edge) { // 这里的参数是 e的编号!
vis[u] = 1;
for (int e = head[u]; e; e = edges[e].nxt) {
if (e == (in_edge ^ 1)) continue; // 特意处理了大小为2的环,注意这里 (in_edge^1) 需要加括号!
int v = edges[e].to;
if (vis[v]) {
if (!cycle.size()) { // 只跑一个cycle!因为有重边!
int c = u;
while (c != v) {
cycle.push_back(c);
c = pre[c];
}
cycle.push_back(c);
for (int j : cycle) iscycle[j] = 1;
}
} else {
pre[v] = u;
dfs1(v, e); // 注意这里参数是 e
}
}
}
有向图找环
只考虑没有重边的情况,那么就用染色来做。没有访问的染色为 $0$,已经访问了并且在栈里的染色为 $1$,已经访问了,但不在栈里的染色为 $2$。
然后只用做一次 dfs 就可以了(最小环需要 $n$ 次)。
