Trie 和 01 Trie
Contents
介绍
01-Trie 指将整数拆成二进制,然后将二进制以字符串的形式储存在 Trie 中。
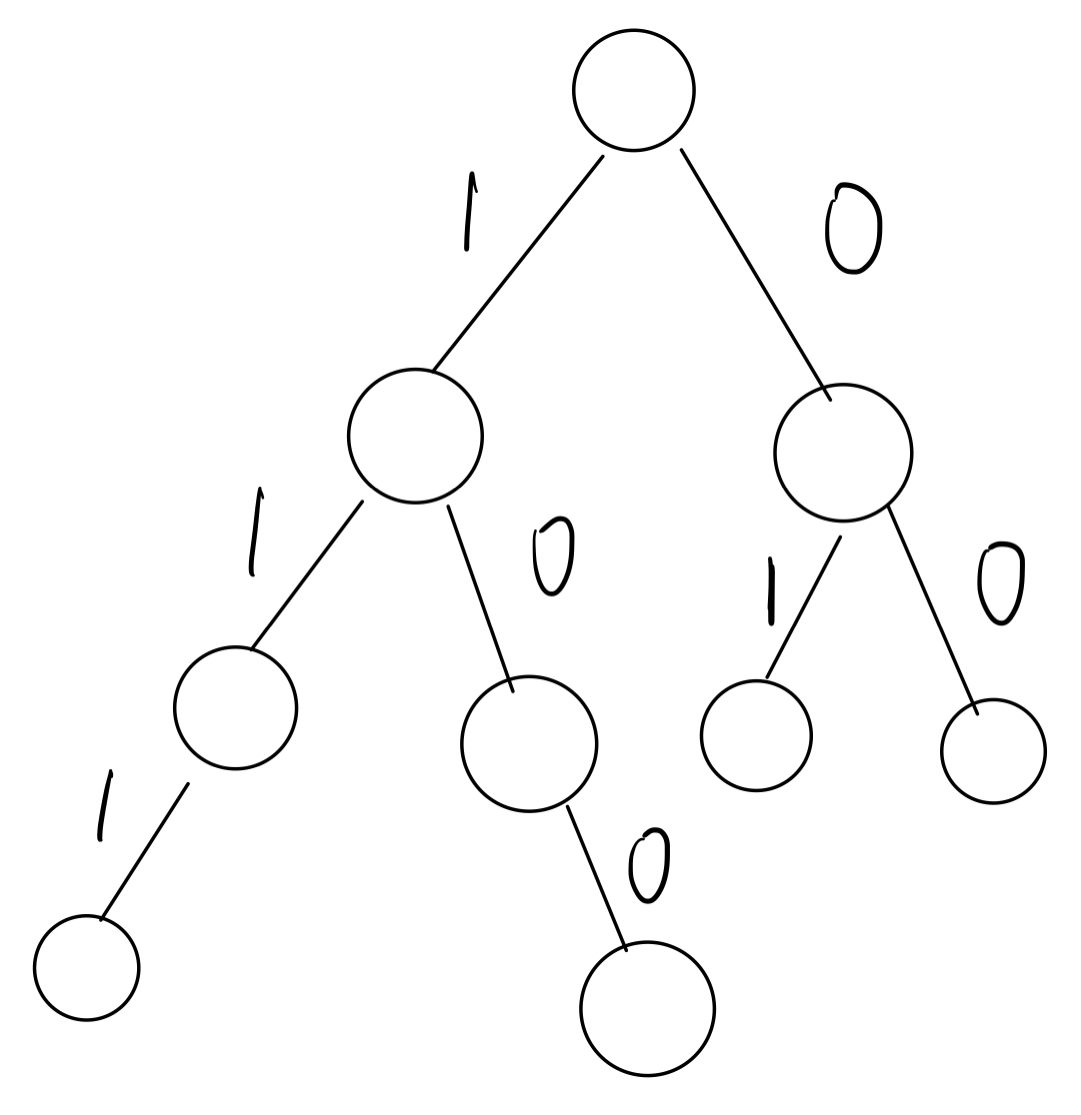
Trie可以解决以下问题:
-
给定一些数 $a_1,a_2,…,a_n$,给定 $x$,求 $a_i$,使得 $a_i \text{ xor } x$ 最大。
-
维护异或和:给定一些数,支持全体加一,插入数字,删除数字,求全体异或和等操作。
Trie可以将数字从低位到高位储存,也可以反过来,根据具体题目而定。
为了方便,我们在写 01Trie 的时候都会把每个数补成同样的位数。
• 注意 id = 1 的是 Root,所以 id 要从 $1$ 开始。
维护最大XOR
指第一个例子,这里我们的 01Trie 将会 从高位到低位 储存。
在给定一个查询 $x$ 时,我们从 $x$ 的高位开始看,设当前到了第 $i$ 位,那么我们看第 $i$ 位的bit $a_i$,然后判断一下第 $i$ 位的值为 a[i] ^ 1 的数字是否存在即可,如果存在,往那个方向走,否则往另外一个方向走。
板子
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int maxn = 1e5+5;
int id = 1; // 注意,从 1 开始
struct Node {
int cnt = 0;
int child[2];
} trie[maxn<<4];
void insert(int x) {
int c = 1;
for (int j = maxm; j >= 0; j--) {
int k = 0;
if (x & (1<<j)) k = 1;
if (!trie[c].child[k]) trie[c].child[k] = ++id;
c = trie[c].child[k];
trie[c].cnt++;
}
}
// 求 trie中的一个数 a_i, 使得 a_i ^ x 最大
int query(int x) {
int c = 1;
int res = 0;
for (int j = maxm; j >= 0; j--) {
int k = 0;
if (x & (1<<j)) k = 1;
k ^= 1;
if (trie[c].child[k]) {
c = trie[c].child[k];
res |= (1<<j);
} else {
c = trie[c].child[k^1];
}
}
return res;
}
维护XOR和
指第二个例子,这里我们的 01Trie 从低位到高位储存。
要维护异或和,我们只需要知道每一位上 $0$ 和 $1$ 个数的奇偶性即可。
对于每一个节点,我们记录三个量:
- 两个子节点的编号
w:指当前这个节点,到它的parent这条边 $(p,u)$ 上,被经过的次数。每有一个数字在插入过程中经过这个边,这个w就会加一。val:指以当前节点为根,它子树内包含的所有数字的 XOR和。
所以维护信息的时候就有:
void push_up(int cur) {
trie[cur].val = trie[cur].w = 0; // 先清空
int c0 = trie[cur].child[0], c1 = trie[cur].child[1];
// 更新 w
if (c0) trie[cur].w += trie[c0].w;
if (c1) trie[cur].w += trie[c1].w;
// 更新 val
if (c0) {
trie[cur].val ^= (trie[c0].val << 1);
}
if (c1) {
trie[cur].val ^= ((trie[c1].val << 1) | (trie[c1].w & 1)); // 如果 c1 的 w 为奇数,就提供了 1 的贡献
}
}
解释: 注意是从低位到高位储存的,所以子树内储存的只是数字的二进制的一部分。
所以要把 val 进行左移。
也就是说,实际上只有 根节点 的 val 是真正有意义的,因为只有根节点才记录的是完整的数字的 XOR和。
插入和删除就不提了,看代码即可。注意插入删除合并起来,可以达成单点修改的效果。
最后说一下全局加一。
全局加一指的是将整个01Trie维护的所有数字都加一。
在二进制下的加一,相当于从低位到高位找第一个出现的 $0$,然后将其变成 $1$。
最后,比这一位低的所有位都将会从 $1$ 变成 $0$。
// add 1 to all numbers maintained by cur
void addall(int cur) {
swap(trie[cur].child[0], trie[cur].child[1]);
if (trie[cur].child[0]) {
addall(trie[cur].child[0]);
}
push_up(cur);
}
板子
const int M = 21; // 最大深度
int id = 0;
struct Node {
int w; // 到 parent 这条边上的个数
int val; // subtree 内的XOR和
int child[2];
} trie[maxn*(M+1)];
void push_up(int cur) {
trie[cur].val = trie[cur].w = 0; // 先清空
int c0 = trie[cur].child[0], c1 = trie[cur].child[1];
// 更新 w
if (c0) trie[cur].w += trie[c0].w;
if (c1) trie[cur].w += trie[c1].w;
// 更新 val
if (c0) {
trie[cur].val ^= (trie[c0].val << 1);
}
if (c1) {
trie[cur].val ^= ((trie[c1].val << 1) | (trie[c1].w & 1)); // 如果 c1 的 w 为奇数,就提供了 1 的贡献
}
}
// cur: index, x: 当前的数字, dep: 深度
void insert(int& cur, int x, int dep) {
if (!cur) cur = ++id;
if (dep >= M) {
trie[cur].w++; // w += 1
return;
}
int c = x & 1;
insert(trie[cur].child[c], (x>>1), dep+1);
push_up(cur);
}
void del(int& cur, int x, int dep) {
if (!cur) cur = ++id;
if (dep >= M) {
trie[cur].w--; // w -= 1
return;
}
int c = x & 1;
insert(trie[cur].child[c], (x>>1), dep+1);
push_up(cur);
}
// add 1 to all numbers maintained by cur
void addall(int cur) {
swap(trie[cur].child[0], trie[cur].child[1]);
if (trie[cur].child[0]) {
addall(trie[cur].child[0]);
}
push_up(cur);
}
可持久化01-Trie
和主席树相似,可持久化01-Trie主要是为了让我们获得任何一个区间 $[L,R]$ 内组成的 01-Trie。
使用 Node 的 cnt 来决定 01-Trie 的内容。
板子
const int maxn = 6e5+5;
const int M = 28;
struct Node {
int cnt;
int child[2];
} trie[maxn * (M+3)];
int n, q, root[maxn], a[maxn], id;
void insert(int pre, int cur, int x) {
for (int i = M; i >= 0; i--) {
int c = 0;
if (x & (1 << i)) c = 1;
trie[cur].cnt = trie[pre].cnt + 1; // cnt 加一
if (!trie[cur].child[c]) trie[cur].child[c] = ++id; // 新建节点
trie[cur].child[c^1] = trie[pre].child[c^1]; // 复制另外一个子节点
cur = trie[cur].child[c];
pre = trie[pre].child[c];
}
trie[cur].cnt = trie[pre].cnt + 1;
}
// find the maximum value for a ^ x (a is in [pre, cur])
int query(int pre, int cur, int x) {
int res = 0;
for (int i = M; i >= 0; i--) {
int c = 0;
if (x & (1 << i)) c = 1;
c ^= 1;
if (trie[trie[cur].child[c]].cnt - trie[trie[pre].child[c]].cnt) { // cnt > 0
cur = trie[cur].child[c];
pre = trie[pre].child[c];
res |= (1<<i);
} else {
cur = trie[cur].child[c^1];
pre = trie[pre].child[c^1];
}
}
return res;
}
int main() {
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
cin >> a[i]; sum[i] = sum[i-1] ^ a[i];
if (!root[i]) root[i] = ++id;
insert(root[i-1], root[i], sum[i]);
}
// 查询 [L,R] -> (l-1,r)
int res = query(root[max(0,l-1)], root[r], x);
}
例题
例1 洛谷P4551 最长异或路径
题意
给定一个 $n$ 个节点的树,边上有权值。
寻找树上的两个节点,使得路径上的边权 XOR和 最大,输出这个最大值。
其中,$n \leq 10^5$。
题解
常见套路:设 $f_x$ 为从 $1$(根节点)到 $x$ 的路径上的 XOR和。
那么 $(u,v)$ 路径上的 XOR和 就等于 $f_u \text{ xor } f_v$。因为 $1$ 到 $LCA(u,v)$ 的部分被抵消掉了。
所以就相当于建立一个 01Trie,储存所有的 $f_u$,然后对于每个 $u$,都询问一下最大的XOR即可。
代码
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const ll mod = 1e9+7;
const int maxn = 1e5+5;
const int maxm = 30;
struct Edge {
int to, nxt, w;
} edges[maxn<<1];
int head[maxn], ecnt = 1, n;
void addEdge(int u, int v, int w) {
Edge e = {v, head[u], w};
edges[ecnt] = e;
head[u] = ecnt++;
}
int dp[maxn];
void dfs(int u, int p) {
for (int e = head[u]; e; e = edges[e].nxt) {
int to = edges[e].to;
if (to == p) continue;
dp[to] = dp[u] ^ edges[e].w;
dfs(to, u);
}
}
int id = 1;
struct Node {
int cnt = 0;
int child[2];
} trie[maxn<<4];
void insert(int x) {
int c = 1;
for (int j = maxm; j >= 0; j--) {
int k = 0;
if (x & (1<<j)) k = 1;
if (!trie[c].child[k]) trie[c].child[k] = ++id;
c = trie[c].child[k];
trie[c].cnt++;
}
}
int query(int x) {
int c = 1;
int res = 0;
for (int j = maxm; j >= 0; j--) {
int k = 0;
if (x & (1<<j)) k = 1;
k ^= 1;
if (trie[c].child[k]) {
c = trie[c].child[k];
res |= (1<<j);
} else {
c = trie[c].child[k^1];
}
}
return res;
}
int main() {
fastio;
cin >> n;
for (int i = 1; i <= n-1; i++) {
int u,v,w; cin >> u >> v >> w;
addEdge(u,v,w); addEdge(v,u,w);
}
dfs(1, 0);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) insert(dp[i]);
int ans = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
ans = max(ans, query(dp[i]));
}
cout << ans << endl;
}
例2 CF817E Choosing The Commander
题意
给定 $q$ 个询问,共有3种:
$1 ~ p$:将 $p$ 加入集合。
$2 ~ p$:将 $p$ 从集合中删除。
$3 ~ p ~ l$:询问集合中有多少个元素在 XOR $p$ 之后小于 $l$。
其中,$q \leq 10^5$。
题解
在 01-Trie 每个节点处加上一个 count 就可以了。
代码
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int maxn = 2e5+5;
const int maxm = 27;
int Q, id = 1;
struct Node {
int child[2];
int cnt = 0;
} trie[maxn<<3];
void insert(int x) {
int c = 1;
for (int j = maxm; j >= 0; j--) {
int k = 0;
if (x & (1<<j)) k = 1;
if (!trie[c].child[k]) trie[c].child[k] = ++id;
c = trie[c].child[k];
trie[c].cnt++;
}
}
void del(int x) {
int c = 1;
for (int j = maxm; j >= 0; j--) {
int k = 0;
if (x & (1<<j)) k = 1;
if (!trie[c].child[k]) trie[c].child[k] = ++id;
c = trie[c].child[k];
trie[c].cnt--;
}
}
int query(int p, int l) {
int c = 1;
int res = 0;
for (int j = maxm; j >= 0; j--) {
if (l & (1<<j)) { // 如果这一位有,说明要往这一位为 1 的方向走
int k = ((p & (1<<j)) > 0);
res += trie[trie[c].child[k]].cnt;
if (trie[trie[c].child[k^1]].cnt) c = trie[c].child[k^1];
else break;
} else { // 如果这一位没有,就往 0 的方向走
int k = ((p & (1<<j)) > 0);
if (trie[trie[c].child[k]].cnt) c = trie[c].child[k];
else break;
}
}
return res;
}
int main() {
fastio;
cin >> Q;
while (Q--) {
int op, p, l;
cin >> op >> p;
if (op == 1) {
insert(p);
} else if (op == 2) {
del(p);
} else {
cin >> l;
int res = query(p,l);
cout << res << "\n";
}
}
}
例3 洛谷P6018 [Ynoi2010] Fusion tree
题意
给定一棵 $n$ 个节点的树,每个节点 $i$ 上有权值,初始权值为 $a_i$。
给出 $m$ 个询问,询问的类型有3种:
$1 ~ x$:将所有与节点 $x$ 距离为 $1$ 的节点的权值加一。
$2 ~ x ~ v$:将节点 $x$ 的权值减去 $v$。
$3 ~ x$:询问所有与节点 $x$ 距离为 $1$ 的节点权值的XOR和。
其中,$n,m \leq 5 \times 10^5$,初始权值 $\leq 10^5$。
题解
这里是 01-Trie 用来维护XOR和。
我们可以对于每一个节点,都把它的孩子(距离为 $1$)的XOR和 维护在一个 01Trie里面。
因为 01-Trie 是动态开点的,所以总共复杂度也就 $n\log(10^5)$。
然后因为每个节点都只有一个 parent,就单独维护即可。
然后对于操作 $1 ~ x$,我们需要做的几件事:
- 单独更新 $x$ 的parent。
- 给 $x$ 打上一个懒标记,代表它要给它的孩子加上 $lazy$ 的值。
- 在 $x$ 维护的 01-Trie 上进行全体加一操作。
然后在每次操作之前,都先检查一下 $parent$ 的懒标记,将其下放。
当然这里的下放不太一样,一个节点可能有非常多个孩子,所以我们选择给每一个节点 $x$ 都定义一个值 add[x],代表它已经从parent那里得到了多少下放的懒标记。
然后就给 $x$ 的权值加上 (lazy[p] - add[x])。
代码
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int maxn = 5e5+5;
const int M = 21; // 最大深度
int id = 0;
struct Node {
int w; // 到 parent 这条边上的个数
int val; // subtree 内的XOR和
int child[2];
} trie[maxn*(M+1)];
int root[maxn], lazy[maxn], add[maxn];
void push_up(int cur) {
trie[cur].val = trie[cur].w = 0; // 先清空
int c0 = trie[cur].child[0], c1 = trie[cur].child[1];
// 更新 w
if (c0) trie[cur].w += trie[c0].w;
if (c1) trie[cur].w += trie[c1].w;
// 更新 val
if (c0) {
trie[cur].val ^= (trie[c0].val << 1);
}
if (c1) {
trie[cur].val ^= ((trie[c1].val << 1) | (trie[c1].w & 1)); // 如果 c1 的 w 为奇数,就提供了 1 的贡献
}
}
// cur: index, x: 当前的数字, dep: 深度
void insert(int& cur, int x, int dep) {
if (!cur) cur = ++id;
if (dep >= M) {
trie[cur].w++;
return;
}
int c = x & 1;
insert(trie[cur].child[c], (x>>1), dep+1);
push_up(cur);
}
void del(int& cur, int x, int dep) {
if (!cur) cur = ++id;
if (dep >= M) {
trie[cur].w--;
return;
}
int c = x & 1;
insert(trie[cur].child[c], (x>>1), dep+1);
push_up(cur);
}
// add 1 to all numbers maintained by cur
void addall(int cur) {
swap(trie[cur].child[0], trie[cur].child[1]);
if (trie[cur].child[0]) {
addall(trie[cur].child[0]);
}
push_up(cur);
}
int n, m, a[maxn], par[maxn];
struct Edge {
int to, nxt;
} edges[maxn<<1];
int head[maxn], ecnt = 1;
void addEdge(int u, int v) {
Edge e = {v, head[u]};
head[u] = ecnt;
edges[ecnt++] = e;
}
void dfs(int u) {
for (int e = head[u]; e; e = edges[e].nxt) {
int to = edges[e].to;
if (to == par[u]) continue;
par[to] = u;
insert(root[u], a[to], 0);
dfs(to);
}
}
// modify u to have the value val
void modify(int u, int val) {
// a[u] is previous value
int p = par[u];
if (p) {
del(root[p], a[u], 0);
insert(root[p], val, 0);
}
a[u] = val;
}
int main() {
fastio;
cin >> n >> m;
for (int i = 1; i <= n-1; i++) {
int u,v; cin >> u >> v;
addEdge(u,v); addEdge(v,u);
}
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
cin >> a[i];
}
dfs(1);
while (m--) {
int op, x; cin >> op >> x;
if (op == 1) {
addall(root[x]);
int p = par[x];
if (p) {
a[p] = a[p] + lazy[par[p]] - add[p];
add[p] = lazy[par[p]];
modify(par[x], a[p] + 1);
}
lazy[x]++;
}
if (op == 2) {
int v; cin >> v;
a[x] = a[x] + lazy[par[x]] - add[x];
add[x] = lazy[par[x]];
modify(x, a[x] - v);
}
if (op == 3) {
int res = trie[root[x]].val;
int p = par[x];
if (p) {
a[p] = a[p] + lazy[par[p]] - add[p];
add[p] = lazy[par[p]];
res ^= a[p];
}
cout << res << "\n";
}
}
}
例4 洛谷P4735 最大异或和
题意
给定一个非负整数序列 $a_1,a_2,…,a_n$。
现给定 $m$ 个操作,有以下两种操作类型:
$A ~ x$:在序列末尾添加一个数 $x$。
$Q ~ L ~ R ~ x$:输出一个位置 $p$,满足 $p \in [L,R]$,使得 $a_p \bigoplus a_{p+1} \bigoplus … \bigoplus a_n \bigoplus x$ 最大。
其中,$n,m \leq 3 \times 10^5, a_i \in [0,10^7]$。
题解
可持久化 01-Trie 的模版题。
首先,先考虑前缀XOR数组 $s_i = a_1 \bigoplus a_2 \bigoplus … \bigoplus a_i$。
那么
$$a_p \bigoplus a_{p+1} \bigoplus … \bigoplus a_n \bigoplus x = (s_n \bigoplus s_{p-1}) \bigoplus x$$
所以现在问题就变成:
每次询问 $Q ~ L ~ R ~ x$,输出一个位置 $p$,满足 $p \in [L-1,R-1]$,使得 $(s_n \bigoplus s_{p-1}) \bigoplus x$ 最大。
那就很简单了,令 $y = s_n \bigoplus x$,剩下的就是在一个区间 $[L-1,R-1]$ 内找出一个元素 $s_p$ 使得 $s_p \bigoplus y$ 最大。
对于每一个区间都可以用 01-Trie 解决的问题,就是可持久化 01-Trie了。
最后需要注意一下这个样例:
4 1
2 4 8 16
Q 1 4 1
答案应为 $31$,但我输出 $29$。
这是因为我们要单独处理一下 $s_0$ 的情况。换而言之我们要将 $s_0 = 0$ 插入到 root[1] 当中。
所以 root[1] 需要包含 $2$ 个元素:$s_0,s_1$。
对于一个版本插入 $2$ 个元素,只要在第二次插入时使用 insert(root[1], root[1], 0) 即可。
最后再注意一下一些边界条件如 $[L-1,R-1]=[0,0]$ 即可。
代码
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int maxn = 6e5+5;
const int M = 28;
struct Node {
int cnt;
int child[2];
} trie[maxn * (M+1)];
int sum[maxn]; // sum[n] 代表 a[1] ^ a[2] ... ^ a[n]
int n, q, root[maxn], a[maxn], id;
void insert(int pre, int cur, int x) {
for (int i = M; i >= 0; i--) {
int c = 0;
if (x & (1 << i)) c = 1;
trie[cur].cnt = trie[pre].cnt + 1; // cnt 加一
if (!trie[cur].child[c]) trie[cur].child[c] = ++id; // 新建节点
trie[cur].child[c^1] = trie[pre].child[c^1]; // 复制另外一个子节点
cur = trie[cur].child[c];
pre = trie[pre].child[c];
}
trie[cur].cnt = trie[pre].cnt + 1;
}
// find the maximum value for a ^ x (a is in [pre, cur])
int query(int pre, int cur, int x) {
int res = 0;
for (int i = M; i >= 0; i--) {
int c = 0;
if (x & (1 << i)) c = 1;
c ^= 1;
if (trie[trie[cur].child[c]].cnt - trie[trie[pre].child[c]].cnt) { // cnt > 0
cur = trie[cur].child[c];
pre = trie[pre].child[c];
res |= (1<<i);
} else {
cur = trie[cur].child[c^1];
pre = trie[pre].child[c^1];
}
}
return res;
}
int main() {
fastio;
cin >> n >> q;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
cin >> a[i]; sum[i] = sum[i-1] ^ a[i];
if (!root[i]) root[i] = ++id;
insert(root[i-1], root[i], sum[i]);
if (i == 1) insert(root[1], root[1], 0);
}
while (q--) {
char op; cin >> op;
if (op == 'A') {
int x; cin >> x;
a[++n] = x;
sum[n] = sum[n-1] ^ a[n];
if (!root[n]) root[n] = ++id;
insert(root[n-1], root[n], sum[n]);
} else {
int l,r,x; cin >> l >> r >> x;
l--; r--;
x ^= (sum[n]);
if (l == 0 && r == 0) {
cout << x << "\n"; continue;
}
int res = query(root[max(0,l-1)], root[r], x);
cout << res << "\n";
}
}
}
例5 CF241B Friends
题意
给定一个长度为 $n$ 的非负整数数组 $a_1,a_2,…,a_n$。
现在选择 $m$ 个pair $(i,j)$,使得这 $m$ 个pair 对应的 $a_i \text{ xor } a_j$ 值的 sum 最大。
其中,$n \leq 5 \times 10^4, a_i \leq 10^9$,答案对 $10^9+7$ 取模。
• $(i,j)$ 和 $(j,i)$ 算作一个 pair。
题解
神仙题。
本题要求的是前 $m$ 大的XOR pair的和。
我们先列出本题的过程:
- 求出第 $m$ 大。
- 求出 XOR 小于等于 $x$ 的所有pair的和。
- 对于一个区间 $[L,R]$,在 $O(1)$ 求出 $\sum\limits_{i=L}^R y \text{ xor } a_i$。
第一步:求第 $m$ 大
• 虽然 $(i,j)$ 和 $(j,i)$ 算作一个 pair,但我们只要把所有东西都乘以 $2$ 就行了。所以我们求第 $2m$ 大。
最简单粗暴的方法当然是二分最终的结果 $x$,然后对于每一个 $a_i$,判断一下在 Trie 中有多少个数字和它 XOR 起来 $\geq x$,把这些 count 累加起来然后查看 count >= 2m 与否,来调整 $x$ 的值。
这样的时间复杂度是 $O(n\log^2 10^9)$,本题可过,但是另外一个版本不可过。
于是我们思考一下能不能直接在 Trie 上模拟这个二分的过程来构建最终的结果 $x$。
发现是可以的,我们从高位到低位,枚举每一位取 $1$ 还是 取 $0$。
然后我们对于每一个 $a_i$ 都判断一下 count 的总和,如果 count >= 2m,则说明这一位可以取 $1$。否则的话需要取 $0$,同时问题变成寻找第 $2m - count$ 大(有点类似于主席树寻找第 $k$ 大的思路)。
• 这个过程是在所有 $a_i$ 上进行的,所以我们维护 $n$ 个指针 ptr[] 代表 $a_i$ 目前在 Trie 的什么位置。
复杂度为 $O(n\log 10^9)$。
第二步:求出 XOR 小于等于 $x$ 的所有pair的和
如果这个问题不是求出和,而是求出个数的话,就是例 $2$ 的问题了。
可惜不是,那怎么处理?
一样,我们从每个 $a_i$ 开始进行 check,对于每一个 Trie 上的节点,我们可以维护一个 cnt[31],其中 cnt[j] 代表当前Trie节点的子树里有多少个数字满足第 $j$ 位为 $1$。
这样当然可以算,但是空间复杂度 $O(n\log^2 10^9)$,本题或许可过,但另外一个版本仍然不可过。
我们这里给出一个非常优秀的结论:
如果 $a_i$ 是 sorted 的,那么 Trie 上任意一个节点的子树 对应 $a_i$ 上的一段连续区间。
这个也不难理解,因为 Trie 的一个子树对应的是拥有一个 “特定前缀” (如 “1101”)的所有数字的集合。
有了这个结论以后,我们在枚举 $a_i$ 时,假设我们目前到了第 $j$ 位,就分两种情况:
- $x$ 的第 $j$ 位为 $1$:那么我们就往 $1$ 的方向走。
- $x$ 的第 $j$ 位为 $0$:我们把 $a_i$ XOR 上 $1$ 的那个子树,求出sum,给答案加上,然后往 $0$ 的方向走。
注意到 $a_i$ XOR 上一个子树的 sum,可以转化成一个区间上的问题,那么就有第三步:
第三步:对于一个区间 $[L,R]$,在 $O(1)$ 求出 $\sum\limits_{i=L}^R y \text{ xor } a_i$。
由于 $a_i$ 总共有 $n$ 个,所以不能直接求前缀和。
但我们可以把区间内的每个数都 拆成二进制。
然后对于拆开的二进制,每一位分别 XOR 上 $0$ 和 $1$,然后都进行一个前缀和。
这样给定一个数字 $y$,就可以把 $y$ 拆成二进制,然后对于每一位 $j$,把 $[L,R]$ 内对应的和用 $O(1)$ 时间内求出来即可。
• 所以我们要做的事就是先 sort 一下整个 $a_i$ 数组,然后在构建 Trie 的时候记录一下每个子树对应哪个区间即可。
最后要注意,由于第 $2m$ 大有可能 等于 第 $2m+1, 2m+2 …$ 大,所以要处理掉额外加上的部分。
答案除以 $2$ 即可。
代码
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const ll mod = 1e9+7;
const int maxn = 5e4+5;
const int M = 31;
struct Node {
int cnt = 0;
int child[2];
int L = 1e9, R = -1; // left and right segments
} trie[maxn * (M+1)];
int id = 1;
void insert(int idx, ll x) {
int c = 1;
for (int i = M; i >= 0; i--) {
int k = ((x & (1LL<<i)) ? 1 : 0);
if (!trie[c].child[k]) trie[c].child[k] = ++id;
c = trie[c].child[k];
trie[c].cnt++;
trie[c].L = min(trie[c].L, idx); // 维护子树对应的区间
trie[c].R = max(trie[c].R, idx);
}
}
ll a[maxn];
ll n,m;
// 寻找第 k 大 (本题是找到第 2m 大)
int ptr[maxn]; // 每一个 ai 对应的 Trie 上的 ptr
ll find_kmax(ll t) {
ll res = 0;
fill(ptr+1, ptr+n+1, 1); // 开始都在 1
for (int j = M; j >= 0; j--) {
ll cnt = 0;
// 找这一位 >= 1 的有多少个
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
int k = ((a[i] & (1LL<<j)) ? 1 : 0);
k ^= 1;
cnt += trie[trie[ptr[i]].child[k]].cnt;
}
int nxt;
if (cnt >= t) {
res |= (1LL<<j);
nxt = 1;
} else {
t -= cnt;
nxt = 0;
}
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
int k = ((a[i] & (1LL<<j)) ? 1 : 0);
k ^= nxt; // 由这一步决定的哪一个来判断每一个 ptr 的更新位置
ptr[i] = trie[ptr[i]].child[k];
}
}
return res;
}
int sum[maxn][M+1][2];
// 计算 a[L,R] ^ x 之和
ll sum_range(ll l, ll r, ll x) {
ll ans = 0;
for (int j = M; j >= 0; j--) {
int k = ((x & (1LL<<j)) ? 1 : 0);
ll s = sum[r][j][k] - sum[l-1][j][k];
ans += s * (1LL << j);
ans %= mod;
}
return ans;
}
ll qpow(ll a, ll b) {
ll res = 1;
while (b) {
if (b & 1) res = res * a % mod;
a = a * a % mod;
b >>= 1;
}
return res;
}
// 获得 ai ^ aj >= x 的所有数之和
ll get_sum(ll x) {
// 先把每个数拆成二进制,做前缀和
for (int j = M; j >= 0; j--) {
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
for (int k = 0; k <= 1; k++) {
int c = ((a[i] & (1LL<<j)) ? 1 : 0);
c ^= k;
sum[i][j][k] = sum[i-1][j][k] + c;
}
}
}
ll ans = 2 * x % mod;
ll cnt = 0; // 使用的对数
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
int c = 1;
for (int j = M; j >= 0; j--) {
int k = ((a[i] & (1LL<<j)) ? 1 : 0);
int d = ((x & (1LL<<j)) ? 1 : 0);
if (d == 0) {
// 加上所有 xor 起来为 1 的部分, 然后走到 0
int p = trie[c].child[k^1];
if (p) {
ans += sum_range(trie[p].L, trie[p].R, a[i]);
cnt += (trie[p].R - trie[p].L + 1);
ans %= mod;
}
c = trie[c].child[k];
} else {
c = trie[c].child[k^1];
}
}
}
cnt += 2;
ans = (ans - ((cnt - 2 * m) % mod * x % mod) + mod) % mod; // 减去重复的部分
ans = ans * qpow(2, mod-2) % mod;
return ans;
}
int main() {
cin >> n >> m;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) cin >> a[i];
if (!m) {
cout << 0 << endl;
return 0;
}
sort(a+1, a+n+1);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) insert(i, a[i]);
ll x = find_kmax(2 * m);
ll ans = get_sum(x);
cout << ans << endl;
}
例6 CF1625D Binary Spiders
题意
给定 $n$ 个非负整数,和一个非整数 $k$。
求 $n$ 个非负整数的一个 subset,使得这个 subset 最大,并且 subset内 每两个数之间的 XOR $\geq k$。
其中,$n \leq 3 \times 10^5, k,a_i \in [0,2^{30}-1]$。
题解
首先我们设 $k$ 的最高位为 $j$。
那么我们将所有的 $a_i$ 分成三个部分:
- 最高位 $\geq j+1$ 的。
- 最高位 $= j$ 的。
- 最高位 $\leq j-1$ 的。
那么我们可以发现,对于 Case 2, Case 3,各只能最多选出 $1$ 个数来。
那么对于 Case 1 呢?
不如我们只考虑它们 bitmask的 prefix,即 $[j+1,30]$ 的这一部分。
我们注意到,如果两个 prefix 不同的数,一定是可以共存的。
如果两个数的 prefix 相同呢?是 有可能 可以共存的!
更准确的来说,如果两个数的 prefix 相同,我们可以把这部分抵消掉,那么问题就变成了最高位 $\leq j$ 的一些数可以最多选多少个出来共存。
这实际上就是 Case 2 和 Case 3 的并集,我们很容易发现这个并集内,最多可以选 $2$ 个数。
所以问题就简化了,我们只要根据 prefix 分类这些数,然后在每个分类中,选出最多两个数来即可。
而选择最多两个数判断是否 $\geq k$,用 01-Trie 可以轻松解决。
实现的过程:
- 先找出 $k$ 的最高位 $j$。
- 将所有的数字按照 $[j+1,30]$ 这一部分的prefix分类。
- 对于每一类,都构建 01-Trie 判断是否存在两个数的 XOR $\geq k$,存在就选择这两个数,否则只选一个。
代码
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int maxn = 3e5+5;
const int maxm = 30;
int id = 1; // 注意,从 1 开始
struct Node {
int cnt = 0;
int child[2];
} trie[maxn<<4];
void insert(int x, int delta) {
int c = 1;
for (int j = maxm; j >= 0; j--) {
int k = 0;
if (x & (1<<j)) k = 1;
if (!trie[c].child[k]) trie[c].child[k] = ++id;
c = trie[c].child[k];
trie[c].cnt += delta;
}
}
// maximum query
int query(int x) {
int c = 1;
int res = 0;
for (int j = maxm; j >= 0; j--) {
int k = 0;
if (x & (1<<j)) k = 1;
k ^= 1;
if (trie[trie[c].child[k]].cnt) {
c = trie[c].child[k];
res |= (1<<j);
} else {
c = trie[c].child[k^1];
// res |= (1<<j);
}
}
return res;
}
int n,k;
struct Nd {
int val, id;
} a[maxn];
int b[maxn];
vector<int> ans;
vector<pii> vec[maxn];
int main() {
fastio;
cin >> n >> k;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) cin >> a[i].val, a[i].id = i;
sort(a+1, a+n+1, [](auto a, auto b) {
return a.val > b.val;
});
if (k == 0) {
cout << n << endl;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) cout << i << " ";
cout << endl;
return 0;
}
int p = 0;
for (int j = 0; j <= 30; j++) {
if (k & (1<<j)) p = j;
}
int ptr = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
b[i] = a[i].val;
for (int j = 0; j <= p; j++) {
if (b[i] & (1<<j)) b[i] ^= (1<<j);
}
if (!(i > 1 && b[i] == b[i-1])) {
++ptr;
}
vec[ptr].push_back({a[i].val, a[i].id});
}
for (int i = 1; i <= ptr; i++) {
if (vec[i].size() >= 2) {
bool ok = 0;
for (int j = 0; j < vec[i].size(); j++) {
if (!ok && query(vec[i][j].first) >= k) {
for (int a = 0; a < j; a++) {
if ((vec[i][j].first ^ vec[i][a].first) >= k) {
ans.push_back(vec[i][j].second);
ans.push_back(vec[i][a].second);
ok = 1;
break;
}
}
}
insert(vec[i][j].first, 1);
}
if (!ok) {
ans.push_back(vec[i][0].second);
}
for (int j = 0; j < vec[i].size(); j++) {
insert(vec[i][j].first, -1);
}
} else if (vec[i].size() == 1) {
ans.push_back(vec[i][0].second);
}
}
if (ans.size() <= 1) cout << -1 << endl;
else {
cout << ans.size() << endl;
for (int j : ans) cout << j << " ";
cout << endl;
}
}
例7 CF1665E. MinimizOR
题意
给定 $n$ 个非负整数 $a_1,a_2,…,a_n$ 和 $q$ 个询问,每次询问 $[l_i, r_i]$ 之间,选出两个index $j \neq k$,使得 $j,k \in [l_i, r_i]$ 且 $a_j | a_k$ 最小,求最小值。
其中,$n \in [2, 10^5], a_i \in [0, 2^{30}), q \in [1, 10^5], 1 \leq l_i < r_i \leq n$。
题解
可持久化01-trie。
可持久化保证了我们可以对于每一个区间找 $a_j | a_k$ 最小值。
怎么找呢?
考虑从 01-trie 上开始 dfs,如果发现 $0$ 对应的子树中有 $\geq 2$ 个数字,那么说明这一位可以取 $0$,否则只能取 $1$。
但有的情况下,$0$ 对应的子树中只有 $1$ 个数字 $a$,此时我们只能取 $1$,但是这个数字 $a$ 也是要拿出来的,因为它有可能在下一层被用到,所以我们单独用一个 vector<int> tmp 来储存这些 $a$。
最后注意一下,当我们在某一层取了 $0$ 时,要重新判断一下 tmp 中的数字 $a$ 在这一位是否为 $1$,如果是,说明最终答案中一定不可能考虑到这个数字 $a$,扔掉即可。
代码
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int maxn = 1e5+5;
const int M = 30;
struct Node {
int cnt;
int child[2];
} trie[maxn * (M+1)];
int n, root[maxn], id;
void insert(int pre, int cur, int x) {
for (int i = M; i >= 0; i--) {
int c = 0;
if (x & (1 << i)) c = 1;
trie[cur].cnt = trie[pre].cnt + 1; // cnt 加一
if (!trie[cur].child[c]) trie[cur].child[c] = ++id; // 新建节点
trie[cur].child[c^1] = trie[pre].child[c^1]; // 复制另外一个子节点
cur = trie[cur].child[c];
pre = trie[pre].child[c];
}
trie[cur].cnt = trie[pre].cnt + 1;
}
// find the maximum value for a ^ x (a is in [pre, cur])
int query(int pre, int cur, int x) {
int res = 0;
for (int i = M; i >= 0; i--) {
int c = 0;
if (x & (1 << i)) c = 1;
c ^= 1;
if (trie[trie[cur].child[c]].cnt - trie[trie[pre].child[c]].cnt) { // cnt > 0
cur = trie[cur].child[c];
pre = trie[pre].child[c];
res |= (1<<i);
} else {
cur = trie[cur].child[c^1];
pre = trie[pre].child[c^1];
}
}
return res;
}
int ans = 0;
vector<int> tmp, tmp2;
void dfs(int pre, int cur, int d) {
if (d < 0) return;
int cnt0 = 0, cnt1 = 0;
cnt0 = trie[trie[cur].child[0]].cnt - trie[trie[pre].child[0]].cnt;
cnt1 = trie[trie[cur].child[1]].cnt - trie[trie[pre].child[1]].cnt;
for (int j : tmp) {
if (!(j & (1<<d))) cnt0++;
}
if (cnt0 >= 2) {
tmp2.clear(); // 如果为0,这里只能保留这一位为0的!
for (int j : tmp) {
if (!(j & (1<<d))) tmp2.push_back(j);
}
tmp = tmp2;
dfs(trie[pre].child[0], trie[cur].child[0], d-1);
} else {
if (trie[trie[cur].child[0]].cnt - trie[trie[pre].child[0]].cnt) {
assert(trie[trie[cur].child[0]].cnt - trie[trie[pre].child[0]].cnt == 1);
int tcur = trie[cur].child[0], tpre = trie[pre].child[0], tx = ans;
for (int j = d-1; j >= 0; j--) {
if (trie[trie[tcur].child[0]].cnt - trie[trie[tpre].child[0]].cnt) {
tcur = trie[tcur].child[0];
tpre = trie[tpre].child[0];
} else {
tcur = trie[tcur].child[1];
tpre = trie[tpre].child[1];
tx |= (1<<j);
}
}
tmp.push_back(tx);
}
ans |= (1<<d);
dfs(trie[pre].child[1], trie[cur].child[1], d-1);
}
}
void clear(int cur) {
for (int c = 0; c <= 1; c++) {
if (trie[cur].child[c]) clear(trie[cur].child[c]);
}
memset(&trie[cur], 0, sizeof(trie[cur]));
}
void clearall() {
id = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
if (root[i]) clear(root[i]), root[i] = 0;
}
}
void Query(int l, int r) {
ans = 0;
tmp.clear();
dfs(root[l-1], root[r], M);
cout << ans << endl;
}
int T, a[maxn];
int main() {
cin >> T;
while (T--) {
cin >> n;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
cin >> a[i];
if (!root[i]) root[i] = ++id;
insert(root[i-1], root[i], a[i]);
}
int q; cin >> q;
while (q--) {
int l, r; cin >> l >> r;
Query(l, r);
}
clearall();
}
}
例8 UniversalCup 12 N.XOR Reachable
题意
给定 $n$ 个点,$m$ 条边的带权无向图。给定一个非负整数 $K$。
现在给定 $Q$ 个询问,每次询问给定一个非负整数 $D$。对于这次询问,我们保留所有权值为 $C_i$ 的边使得 $C_i \text{ xor } D < K$,然后回答在这个图中,有多少个pair $u,v$ 使得 $u$ 和 $v$ 能够互相到达。
其中,$1 \leq n,m,Q \leq 10^5, K,C_i,D_j \in [0, 2^{30})$。
询问之间互相独立,并且图中可能有重边(无自环)。
题解
首先可以看出要用到 01-Trie。
我们可以考虑将所有的边都存进 01-Trie 里面,然后对于每一个询问我们可以执行一次 DFS 找到所有这样的边。
计算有多少个 $u,v$ 可以互相到达,肯定是维护一个并查集,然后求每个联通块的大小。
但这样复杂度太高了,我们考虑怎么样只跑一次 DFS 就可以回答所有的询问?
发现本题是离线的,我们不妨把所有的询问也存进 01-Trie 里面,并且只存在叶子节点。
然后我们只跑一次 DFS,当我们 DFS 到一个叶子节点的时候,就回答这个叶子节点储存的所有询问。
怎么 DFS 呢?
我们考虑 $K$ 的每一位,我们现在 DFS 到了第 $i$ 位,假设 $K$ 的第 $i$ 位是 $1$。
那么我们在 DFS 的过程中:
- 对于所有第 $i$ 位为 $1$ 的询问 $D$,说明我们应该加上所有第 $i$ 位为 $1$ 的边 $C$,然后继续 DFS 考虑所有第 $i$ 位为 $0$ 的边。
- 对于所有第 $i$ 位为 $0$ 的询问 $D$,说明我们应该加上所有第 $i$ 位为 $0$ 的边 $C$,然后继续 DFS 考虑所有第 $i$ 位为 $1$ 的边。
• 但这样会发现一个问题,我们希望的是 DFS 到询问所在的叶子,在 DFS 过程中加上边,但这样的话需要 DFS 的询问和边不在同一棵子树里,我们无法在知道具体是哪个询问的同时,知道我们加上了哪些边。
所以我们可以先将所有询问 $D$ 执行 D ^= K,相当于将 $K$ 所有为 $1$ 的位置,都在 $D$ 中翻转了一下。
这样我们就得到
- 对于所有第 $i$ 位为 $1$ 的询问 $D$,说明我们应该加上所有第 $i$ 位为 $0$ 的边 $C$,然后继续 DFS 考虑所有第 $i$ 位为 $1$ 的边。
- 对于所有第 $i$ 位为 $0$ 的询问 $D$,说明我们应该加上所有第 $i$ 位为 $1$ 的边 $C$,然后继续 DFS 考虑所有第 $i$ 位为 $0$ 的边。
这样就没问题了。
同理,如果 $K$ 的第 $i$ 位是 $0$,我们不需要加上某一棵子树中的边,直接 DFS 即可,由于 $K$ 的第 $i$ 位是 $0$ 所以 D ^= K 的操作没有影响。
- 对于所有第 $i$ 位为 $1$ 的询问 $D$,DFS 考虑所有第 $i$ 位为 $1$ 的边。
- 对于所有第 $i$ 位为 $0$ 的询问 $D$,DFS 考虑所有第 $i$ 位为 $0$ 的边。
• 注意 DFS 回溯时,还需要把加上的边撤销掉,这个利用可撤销并查集来做就可以了,每次操作时间复杂度 $O(\log n)$。
时间复杂度是多少?
我们只执行一次 DFS,复杂度为 $O(30n)$。
对于每一条边,它只会被它的所有祖先加上,所以总共加上 + 撤销的操作也是 $O(30n)$,总时间复杂度就是 $O(30n \log n)$。
• 最后注意,DFS 的时候如果深度为 $-1$ 说明我们到达了叶子节点(不是深度为 $0$!)。
代码
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int maxn = 1e5+5;
int n, m, K, Q;
struct Edge {
int from, to, w;
};
vector<Edge> adj[maxn];
struct State {
int u, v, szu, szv;
} st[maxm];
ll ans = 0, res[maxn];
ll cal(ll x) {
return x*(x-1) / 2;
}
struct DSU {
int par[maxn], sz[maxn], tail = 0;
inline void init() {
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) par[i] = i, sz[i] = 1;
tail = 0;
}
int finds(int u) {
if (par[u] == u) return u;
return finds(par[u]);
}
void unions(int u, int v) {
u = finds(u), v = finds(v);
if (sz[u] < sz[v]) swap(u,v); // sz[u] >= sz[v]
st[++tail] = {u, v, sz[u], sz[v]};
if (u == v) return;
par[v] = u;
ans = ans - cal(sz[u]) - cal(sz[v]) + cal(sz[u] + sz[v]);
sz[u] += sz[v];
}
void cancel() {
if (tail > 0) {
int u = st[tail].u, v = st[tail].v;
par[v] = v;
if (sz[u] != st[tail].szu) {
assert(sz[u] == st[tail].szu + st[tail].szv);
ans = ans - cal(sz[u]) + cal(st[tail].szu) + cal(st[tail].szv);
}
sz[u] = st[tail].szu;
sz[v] = st[tail].szv;
tail--;
}
}
} dsu;
struct Node {
int cnt = 0;
int child[2];
vector<Edge> vec;
vector<int> que; // queries 的编号
};
const int M = 30;
bool tag[33];
struct Trie01 {
int id = 1; // 注意,从 1 开始
Node trie[maxn<<5];
void insert(Edge e) {
int x = e.w;
int c = 1;
for (int j = M; j >= 0; j--) {
int k = 0;
if (x & (1<<j)) k = 1;
if (!trie[c].child[k]) trie[c].child[k] = ++id;
c = trie[c].child[k];
trie[c].cnt++;
trie[c].vec.push_back(e);
}
}
void insert(int x, int i) {
int c = 1;
for (int j = M; j >= 0; j--) {
int k = 0;
if (x & (1<<j)) k = 1;
if (!trie[c].child[k]) trie[c].child[k] = ++id;
c = trie[c].child[k];
trie[c].cnt++;
}
trie[c].que.push_back(i); // 只保留叶子即可
}
void addall(int u) {
for (Edge e : trie[u].vec) {
dsu.unions(e.from, e.to);
}
}
void clearall(int u) {
for (int i = 0; i < trie[u].vec.size(); i++) dsu.cancel();
}
// 从 d = M 开始 dfs
void dfs(int u, int d) {
if (!u) return;
if (d == -1) { // 走完了,开始统计答案
for (int id : trie[u].que) res[id] = ans;
return;
}
int c[2];
c[0] = trie[u].child[0], c[1] = trie[u].child[1];
if (tag[d]) { // 需要加一边,然后dfs另外一边
for (int o = 0; o < 2; o++) {
addall(c[o^1]);
dfs(c[o], d-1);
clearall(c[o^1]);
}
} else {
dfs(c[0], d-1);
dfs(c[1], d-1);
}
}
} tr;
int main() {
fastio;
cin >> n >> m >> K;
for (int i = 1; i <= m; i++) {
int u, v, w; cin >> u >> v >> w;
adj[u].push_back({u,v,w});
adj[v].push_back({v,u,w});
tr.insert({u,v,w});
}
cin >> Q;
for (int i = 1; i <= Q; i++) {
int D; cin >> D;
D ^= K;
tr.insert(D, i);
}
dsu.init();
for (int i = M; i >= 0; i--) tag[i] = (K & (1<<i));
tr.dfs(1, M);
for (int i = 1; i <= Q; i++) cout << res[i] << "\n";
}
